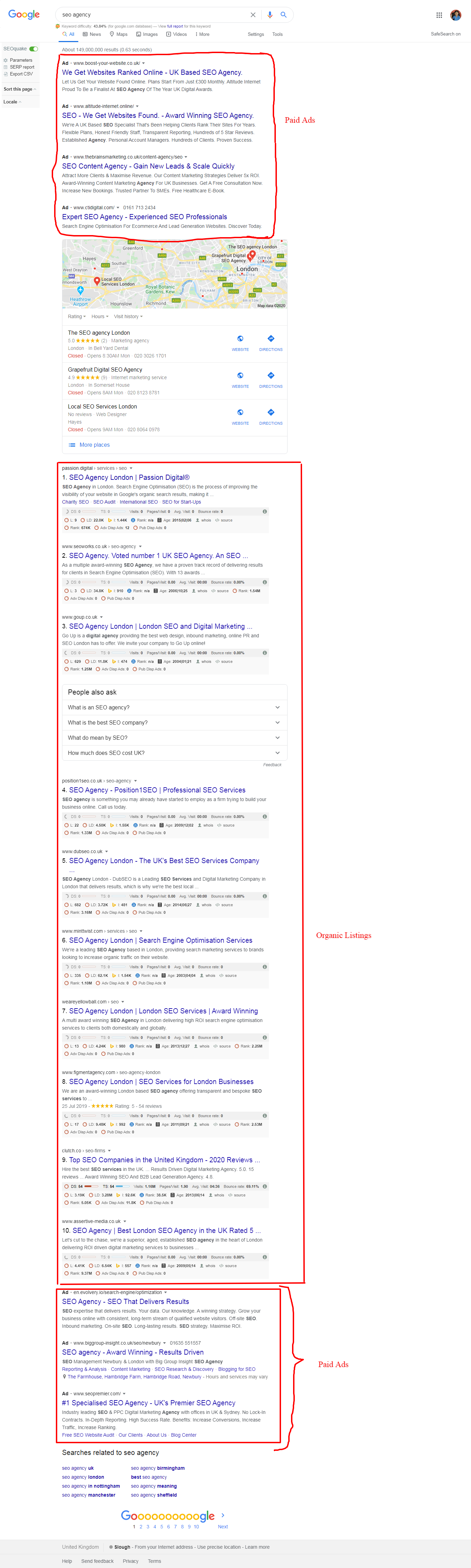
The practice of SEO is to increase a website’s organic search exposure to drive more traffic to the site. Organic search results are completely different from the paid ads often shown in the search engine result pages (SERPs), which are achieved through pay per click (PPC) advertising on the Google Ads platform.
There is a common misconception that the more you pay in Google Ads, the higher up you will appear for your organic results. This is not true at all. They are both completely separate channels.
Paid results appear above and/or below the organic listings. Organic listings and paid listings appear as highlighted in the example below:
Where Every SEO Campaign Should Begin?
Every campaign should start with some extensive keyword research. Until you know what your potential customers are searching for, you can’t guarantee that you are truly targeting them.
Keyword Research
It’s very easy to assume that you know what people are looking for. You could be targeting industry terminology that end users simply don’t know about. On the other hand, you could end up targeting terms that are so competitive that without either a big budget or 12 months’ worth of solid SEO work you have no chance of ranking for them.
Your keyword research can make or break your entire SEO campaign, so you need to spend the time to carry it out effectively.
The aim of this research is to provide you with a list of terms people use to search for your products or services that you can realistically hope to rank for.
The size and authority of your site, as well as the strength of your brand, should also dictate the type of terms you are able to work with.
For example, if you are a small online business with a new website, going after highly generic and competitive terms is going to take a lot of work and patience.
If you are a bigger brand, you possibly have a site in place that already holds some authority and so aiming for the broader, higher search volume terms is going to be a more realistic target.
So what should you do?
A great starting place is to find terms that have a good search volume and a low competition rate.
Suggested Tools
There are a number of free tools you can use to carry out your research including:
- Google Keyword Planner: Google’s own keyword research tool, designed primarily for Google Ads but very useful for SEO targeting too.
- Ubersuggest: This uses the information Google autosuggests when you type a search query into the search engine.
- Google Trends: This shows the popularity of search terms over time.
- Keyword.io: There are both paid and free versions of this tool which you can use to get more keyword insights and ideas.
Remember that the terminology you use within your industry may not be what is used by people searching for your products or services. Brainstorm possible search queries with your team and use this list as starting point.
Once you start to build up a list within the Google keyword planner, you will being to see terms you may not have thought of before, explore these further and you may uncover some gems with high traffic and low competition.
Make sure you work with a truly relevant term for each individual page. Don’t target terms that aren’t relevant simply to try and bring in extra traffic. If it isn’t relevant traffic it could backfire: a high bounce rate could work against you, as well as provide misleading traffic figures.
Once you have your list of terms, it’s time to start looking at the on-page elements.
On-Page SEO Elements
The title tag assigned to each individual page is an important element of SEO.
This tag acts in a couple of ways. Firstly, it describes exactly what searches the page is relevant to. Secondly, it is the beginning of your ‘ad’, that little piece of online real estate within the SERPs that helps to entice potential customers to click through to your page over everyone else.
The important elements to try and include are:
- Company name (for brand promotion)
- Primary targeted key term
- Secondary/related key term (if possible)
The code for a title tag is as follows:
<head>
<title>Digitoly: Digital Marketing & Branding Consulting</title>
</head>
See the example below on how this looks in the SERPs.

The recommended maximum length is 55-65 characters. As the actual number of characters that can fit in the SERPs is based on pixel width, you should check that your page title fits in the SERPs using a preview tool such as the Moz Title Tag Preview Tool Google can also replace your title if it sees fit, often using other page text to make it more relevant to a search query, which is a frustrating issue that can’t be changed.
However, you can minimize the chance of this happened by making your page title as relevant and optimized as possible.
Meta Descriptions
The Meta description tag may no longer hold the SEO value it once did, but it is still a highly important Meta tag. This is basically your sales pitch within the SERPs. This information could be the difference between someone clicking through to your page or to competitors.
Some elements you should try to include are:
- Company name (brand promotion)
- Key term being targeted
- An overview of the page/product you are supplying/service you provide.
- A call to action (CTA) USPs.
The code for this with a title is as follows:
<head>
<title>Digitoly: Digital Marketing & Branding Consultancy</title>
<meta name=”description” content=”We help businesses connect with their audience online – Digital Marketing services, SEO, PPC, Social Media Marketing, Content Marketing, & Brand Building“>
</head>
See below how it will look in the SERPs.

The recommended length is approximately 145-152 characters including spaces. Beyond that, it is likely to be truncated in the SERPs.
Don’t waste this space by filling it with irrelevant information and make sure that what you write really sells your products or services.
Content
When it comes to on-page content, there used to be a number of tick boxes.
- The Keyword in the first sentence
- Keyword in the body text
- Keyword in the final sentence
- Overall keyword density of around 2-3% (depending on the amount of content)
This is no longer the case. Search engines, especially Google, want to write for the user and not for the search engine.
Google is looking for you to provide visitors with a great user experience while, at the same time making sure that the site is accessible to its crawlers. This is fundamentally different from the old days of easy “tick box SEO”, where keyword positioning played its part.
There are, however, certain elements that should still be worked with to help create a natural layout for your page.
Heading
Each page should use heading tags. This helps create a well-structured on-page layout. There are number of heading tags that can be used.
<h1>This is first level heading</h1>
<h2>Second level heading</h2>
<h3>Third level heading</h3>
<h4>Fourth level heading</h4>
<h5>Fifth level heading</h5>
A <h1> heading tag should be used as the main page heading. There should only be one <h1> per page and it should be different from any other page on your site. Beyond that, you should use subheading (<h2>, <h3>, <h4>, <h5>) to break up the text. Use the relevant code depending on their importance within the page.
You should try to include the main key term for that page in the <h1> header, however, do not have a heading tag that is simply the targeted term, unless it’s natural to do so. You are writing for your audience, not search engines.
You can use <h2>, <h3>, etc., as many times as is needed.
On-Page Content
Your aim should be to create fresh and unique content. This means you should write for your audience and create engaging copy.
Google advises against the following:
- Rehashing existing content.
- Having duplicate or near-duplicate versions of your content across your site.
There is no advised keyword density score that you should stick to. Write naturally and don’t add unnecessary keywords.
A good rule of thumb to abide by is: is someone who has no idea about SEO can notice terms sticking out of your content, you haven’t written natural, flowing copy.
Keyword Research
Your initial keyword research should have also been carried out with content in mind.
Did you research relevant keyword variations that could be included within your copy? Remember, the practice of adding a single term as many times as you can is no longer a tactic that will benefit you.
Use the Definitive Guide to Keyword Selection.
So working with variations and synonyms will not only help keep your copy on-topic but also naturally allow you to target further long-tail terms.
If you didn’t do this, revisit your research, and look a little deeper. You may uncover some terms with high search volume and low competition that provide you with easier wins in the long run.
Learn about Semantic Search, as it can affect your SEO efforts.
Images
All images should have alt tags assigned to them. However, make sure you use the alt tag in the correct manner. Years ago, people used to include key terms targeted on that page (within the alt tag) but this isn’t what the tag is for. The tag is to help provide textual information that describes the image.
If you are using images that truly relate to the content of the page, you should be able to include key terms naturally without trying to crowbar them in.
HTML Sitemap Page
This shouldn’t be confused with an XML sitemap. This is a sitemap on your main website (often using the same design) which lists all the pages within the site.
Sitemaps help both search engines and visitors alike, by providing direct links to all areas of your site.
This can help pages become indexed and direct lost visitors who are looking for certain information or products within your site.
Navigation
You could have completed all the above steps, but if the search engines can’t crawl your site, they won’t be seeing any of your great content any time soon.
Make sure that the site navigation code can be followed by the search engines and that there are no pathways that cause them to get stuck in a continuous loop.
If you are creating a new site, make sure that this is one of the initial requirements when talking with your web developer.
When looking at navigation, you should also discuss pagination. This is the way you can navigate from one post to the next and move between different pages. Ensure this navigation is easy for users and can be understood by search engines by using pagination markup code.
Technical SEO
So, your site looks great, you are targeting all of the optimal search terms and the content is unique and enticing.
However, the back end of your site isn’t search-engine-friendly and suddenly all the hard work could count for nothing.
What should you check and look out for?
- Canonical Domain Issues
- Canonical Tag
- URL Structure
- Rich Snippets
- Schema
- txt File
- XML Sitemap
- Broken Links
- HTML Coding
Canonical Domain Issues
A canonical domain issue comes about when you have two versions of your home page live. For example: https://www.yourdomainname.com and https://yourdomainname.com
Why is this an issue?
Well, if you effectively have two versions of your home page live, you could water down the overall strength this page holds. You could be splitting the link strength that is coming into the site.
Not everyone links correctly and anyone using the version of your domain you don’t wish to be using will be sending the strength of that link to the wrong destination. It could even be seen by search engines as duplicate content.
Redirecting the non “www” version to www.yourdomainname.com using a 301 redirect will clear this issue.
Canonical Tag
The canonical tag comes into use when you have duplicate pages on your site.
This may be the case if you have several pages that include the same product which is listed in a variety of ways – price, colour, size, etc.
If Google has crawled your site thoroughly, it will be more than aware that you have pages with the same content. As a result, you may find that it chooses to index only one version. However, for good housekeeping and to avoid any issues, it is advised that the canonical tag is used.
The tag is used to inform Google which page (of the pages that share identical content) is the master version, the preferred version, and most useful for any related search queries.
The tag should be added to the <head> of each page, highlighting the URL of the main page:
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://www.yourdomainname.com/product”/>
URL Structure
A good URL structure not only helps the search engine note relevance but also helps your visitors.
Your URLs should be set up in a way that informs both search engines and visitors about the subject matter of the page. They should also be as simple as possible.
Your URL can also serve as a factor for people clicking through to your page from the SERPs.
For example, if you were looking for a study-desk and you had the following two URLs to choose from, which one stands out?
https://www.domainname.com/study-desk
https://www.domainname.com/543ismad?id_furniture=768sip=2983849
Include key terms relevant to the page in your URLs. Make sure that you use hyphens (-) instead of underscores (_) in your URLs, as these are easier to read when a URL is linked up.
Rich Snippets
Rich snippets have been designed to give extra information to the searcher before they click through to the page.
Using structured data markup makes it easier for Google to interpret the data it needs to populate these areas in the SERPs giving searchers more information and giving your listing more real estate.
To increase the chance of rich snippets being shown in SERPs, you should mark up your pages and the desired information with one of the following supported formats:
- Microdata
- Microformats
- Resource Description Frameworks (RDFs)
Microformats provide search engines with important information regarding the location of the business. They are bodies of code that wrap around information on a site, such a snippet of information which then has a chance of appearing within Google’s SERPs.
Microformats can promote locations, personal information, and reviews.
Schema
Google currently encourages users to utilize Schema for this coding and a good starting point for marking up your business details and address is here: https://schema.org/LocalBusiness
Once your information is marked up you can test it here.
Robots.txt File
The robots.txt file is one of the most important files a site uses.
The robots.txt file gives all search engine bots instructions on how they can crawl your site. In this file, you can exclude areas and even individual pages from being crawled.
When a search engine bot visits a site, it will look for this file first. Within this file, there should be full instructions on which areas should be crawled and which shouldn’t.
This is a very powerful file and, if not set up correctly, can leave your site uncrawled and therefore not indexed.
Your site may not have this file set up as standard. The file is situated in the root of your site, so you can check by going to the correct URL: https://www.yourdomainname.com/robots.txt
If you don’t have one create one and upload it.
A basic file that gives full access to the search engine bots would look like this:
User-agent:*
Disallow:
Sitemap: https://www.yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml
There are various lists of commands that can be used.
Here are some of the most common commands that you may need to use:
User-agent:*
This indicates that the instructions that follow are for any and all user agents. If you wish to disallow a certain bot, you need to name the bot.
User-agent: googlebot
In this example, we are giving instructions explicitly to Google. Each bot has its own name, so check before adding.
Use-agent:*
Disallow:
This command allows all crawlers to index everything within your site.
User-agent:*
Disallow:/
This disallows all crawlers from indexing any pages within your site.
User-agent: Googlebot
Disallow:/
This disallows Google’s bot from crawling the site.
Disallow:/folder name/
This blocks bots from a specific folder.
Disallow:/folder name/page.html
This blocks one individual page.
Disallow: /*?
This command blocks all URLs that contain “?”.
Disallow: /*.asp$
This command allows you to block any URLs that end in an asp extension.
XML Sitemap
XML sitemaps provide the search engines with a complete map of your site, detailing the locations of all the pages within your site. This file is especially important if the search engines are having trouble crawling your site via the navigation.
A link to this file can also be added to the Robots.txt file: Sitemap:
https://www.yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml
To create a sitemap, you can use Yoast plugin that creates a dynamically updating sitemap, depending on what system your website uses.
Once your sitemap has been created, it should be submitted to the main search engines through their search console or webmaster tools portals (e.g., Google Search Console/Bing Webmaster Tools.)
Sitempas can also contain change frequency, priority and the date a page was last changed.
Broken Links
It is very easy to update your site, remove pages, and think nothing more of it. However, updates, pages removal, or just a revamp can leave your site with a trail of broken links.
A broken link is essentially a link that leads to a page on your site that no longer exists.
This can give the impression that your site isn’t well maintained.
The best course of action is to set up 301 redirect commands that inform the search engines that the page being linked to is either no longer live or has moved. The 301 command then redirects the search engines to the new destination.
This is also essential from a user experience point of view as you can ensure that you send the visitor to a working page.
There will also be occasions when external sites imply try to link to a page on your site but don’t include the correct URL. This of course is out your hands, but you should still create 301 redirects to fix this. Suggested tools include:
- Google search console
- DeepCrawl
- Xenu
HTML Coding
Having clean code is also an important element.
Untidy coding or simply incorrect coding can not only affect the look of your site but can also indicate to the search engines that the site isn’t very well maintained.
You may find that some of the coding that isn’t quite up to W3C standards doesn’t really affect the look of a site or the way it works, but considering the number of ranking factors you are up against, you should aim to have clean code.
Bad coding can also stop search engines from crawling your site, it is recommended that you check your coding using the W3C validator tool:
SEO Tools
All of the above suggestions could be followed to the letter, but unless you are able to monitor your site’s performance, you will have no idea where you stand.
There are free tools that are compulsory for any site owner (especially if you are running on online business)
Google Search Console
Google Search Console is free but you do need to have a Google account to set it up for your site.
Search console will provide you with a huge amount of valuable information relating to how Google sees your site, form broken links to what backlinks your site is receiving if there is an issue with your site, you will more often than not find the reason here.
If you don’t create an account for your site, you are pretty much-sailing solo. This is, after all, information directly from Google. They hardly ever release information that actually guides you, so when they do, you need to take advantage of it.
Your account will also provide you with alerts related to your site. If Google is having trouble crawling your site, if it feels like you have unnatural links, or if your robots.txt file is suddenly blocking their crawler (and more), Google will provide you with alerts.
Google Analytics
Google Analytics provides you with traffic statistics for your website.
If you don’t know how many people are coming to your site, what source they come from, how engaged they are with your site, how can you be sure that your site is performing to its full potential?
Google Analytics is another free tool, so there is no reason not to use it.
You will be required to add some code to every page on your site to allow Google to record your traffic statistics. It is important that it is implemented correctly otherwise you run the risk of it not working at all or reporting back incorrect data.
What Else Should You Be Doing?
No campaign is complete unless you know how you fare against your competition. This analysis should form part of your initial work and your ongoing improvements.
When you first enter into SEO, you need to know how strong the competition is, as this could help mould your initial keyword targets. Going after more generic terms against a very strong competitive field could leave you lost in a contest you can’t win any time soon and with no return.
Competitor Analysis
Alternatively, this research could help give you the confidence to go for more generic, broader terms if the competition isn’t as strong as expected or if your site is optimized.
The type of information you want to be looking for to give you an overall picture of how you currently stand against the others includes:
- Domain age – longevity of a domain impacts authority
- Competitor’s overall SEO – title tags, meta descriptions, on-page factors, etc.
- Incoming links
- Content distribution
- Social presence
- Online profiles
- Their rankings
This information will give you a rounded picture of how the competition is performing, how long they have been around, where they are receiving their links, the type of links, how social they are, how they rank, and where they are distributing content.
With this information, you can make far more informed decisions on how you can mould your campaign to take on your competition.
Suggested tools include:
- Majestic
- Social Mention
- Google Alerts
Rank Checking
It is important to keep yourself up to date with your rankings. You have put all this work into optimizing, so you need to know where you rank to see what is working and what isn’t.
If you are targeting only a couple of terms, you may be happy simply to carry out a manual search. However, the majority of SEO campaigns are targeting a high number of terms, so save yourself time and use a rankings tool. Even though you have tools to hand that you can set to check your rankings on a regular basis, it is important not to become obsessed with your rankings.
Rankings fluctuate all the time and any work you carry out isn’t realistically going to affect anything overnight. If you check every day and judge your work on the daily ups and downs, you will get into the habit of making unnecessary changes as a reaction to search engine noise.
Be realistic check every week or beyond and only react to large-scale trends or anomalies, rather than daily fluctuations.
Suggested tools include:
- AccuRanker
- Moz Rank Tracker
- SEMrush
- SERPS Rank Checker
Link Building
All SEO campaigns need to work in conjunction with a security planned link building strategy.
Link building creates incoming links and signals that are paramount to building the strength of your site and developing much-needed relevance and authority.
This is also integral to building your brand.
Originally, link building was all about gaining as many links as possible: finding directories, commenting on blogs and forums, whilst including a keyword-rich another text link back to your site. But now it is no more valid and in practice.
Google wants you to work for your links and create something beneficial. Content is now a big prayer and creating great content that people will engage with and share is now a significant part of any link building strategy.
Working with content also gives you the opportunity to become a voice in your industry or sector.
Although content is now a great way to build links, it is significant you vary your activity. Don’t just find a platform, build a link, and leave, you should be regularly engaging.
You also need to think about where you are building your links. Quality is far better than quantity.
Take into consideration the type of links you are creating. You shouldn’t actively build keyword-rich links anymore, which can be a negative signal that puts you at risk of receiving a ranking penalty. You should instead focus on strong, branded links and citations, with surrounding content that builds contextual relevancy about your offering.
Social Signals
Social signals also play a big part and should form part of your Link building strategy.
Areas to think about as part of your link building strategy include:
- Building business profiles on reputable directories
- Keeping any local listings up to date
- Claiming a presence on all social profile sites for your brand
- Link bait (i.e., producing content with a high likelihood of influencers linking to the piece)
- Local link building (e.g., local press mentions, local bloggers)
- Social signals
- Infographics
- Surveys and questionnaires
- Engaging blog content
- Interesting images
- Press releases (nofollowed links or citations only).
Using Social Signals
Using social as part of your online marketing strategy has now become almost unavoidable.
Social signals created by the activity on popular social platforms are generally believed to have a positive effect on organic rankings. As with SEO, there are many factors that come into play, but the only constant is that you need to have a strong presence socially and you need to engage with your audience.
Linking Your Site to Social Media Channels
It is significant to include links to your social channels on your website to encourage visitors on your site to engage with you. Search engines also use these links to confirm that you are the owner of the social profiles that you have registered.
All Social Media channels are not equally significant for every business to be present on. This guide of Which Social Media Network is Best for Your Business?
To help people find your profiles, you can add links to them in the footer of every page.
Social Sharing
You should also include social sharing functionality in your blog posts and product pages which people would love to share on their social media or with friends.
Google Algorithm Updates
Google keeps updating its algorithm to make the user experience better. The most recent ones are the penguin and Panda updates and after that Google is constantly revising these which shake up the SERPs. It is important to keep yourself updated about these algorithm changes.
If you have an online business and you rely on appearing well within Google, it is a no-brainer that you need to stay up to date with what is going on.
Don’t rest on your laurels for even one second. Just because you are ranking well today doesn’t mean and update won’t come along and change everything. Even if you have an agency looking after your online marketing you should still be keeping yourself up to date.
Below is the website you should bookmark and check regularly:
https://webmasters.googleblog.com/
Black Hat SEO
You may have heard people speak about the white hat and black hat SEO techniques.
White hat techniques are those that are carried out within the Google guidelines and best practices, and as such, they minimize the risk of a site being hit by any penalty.
Black hat SEO is the practice of gaining higher search engine positions through the use of techniques seen as unethical by Google and other search engines.
For every white hat technique, there is a black hat alternative. Which ones you use are solely at the discretion of the site owner. Black hat is usually used to gain quick rankings and results with a very short life span, sometimes literally only days.
As these tactics go against search guidelines, if Google does catch up with you, you can be sure that there will be a reaction against your site.
There is a market for both black and white hat SEO and to suggest otherwise would be naive. But it is highly recommended by reputable search engine specialists that you stick to trusted white hat techniques to work on long-term, sustainable success.
Tactics to Avoid
There are some tactics that can be classed as the black hat that could be used innocently through ignorance but could end up costing you your rankings. These are tactics that you should avoid. They don’t offer any quick results or payback and will work against you in the long run.
Hidden/Invisible Text
This should need a great deal of explaining if you try and hide anything, expect to get caught and expect to be penalized.
There is only one reason why you would hide anything and that is to game the system.
Beware – there are developers out there who claim they can hide information from the search engines, or show information to the search engines but not to users. If this is truly the case, why have it at all? If it is so well hidden that search engines can’t find it, they also can’t read it or count it as a ranking factor. And if users shouldn’t see it, the content obviously isn’t created with the user in mind.
Doorway Pages
These are basically landing pages created for the sole purpose of redirecting potential visitors to your site through niche or locally targeted keywords.
These are designed with only Google and other search engines in mind. More often than not, these pages will be using all the frowned-upon techniques possible to rank highly and quickly. They don’t last or rank for long.
This is now a relatively old technique and isn’t seen as much anymore, however, there are still those who will try to convince you that this is the way forward ignore them.
This is especially true since Google reclassified and targeted sites trying to use doorway pages to rank.
Keyword Stuffing
Remember when we spoke about writing for your audience and not search engines? This is the complete opposite.
Stuffing a page with targeted terms will in fact end up having the opposite effect, as Google can easily understand when content is unnatural.
Invisible Links
Again the act that you are hiding something instantly sets alarm bells ringing.
The only reason you would include a hidden link is that you want the link to be followed (to pass on link strength) but you don’t want it visible to the visitor. Well, if you don’t want the visitor to see it, it shouldn’t be there.
SEO Myths
As well as all the information included within this digital marketing guide, it is important you continue to research the subject of SEO. Like anything within this industry, things change all the time, so it is important you stay up to date.
However, be careful about what you read and what you believe.
Before you do anything, note the date of the blog post you are about to read. How old is it? You could be reading a great post on the importance of ranking for misspellings, but the post was written back in 2010. Whatever you read, make sure it is recent or try to find a more recent piece on the subject to verify that the content is still relevant.
You will also find a lot SEO myths on your travels. Again the date of the post will be e clue, but on the next page we have listed some of the most common myths so you can avoid them.
It’s OK To Pay For Links
Paying to have a link to your site included on another site can get you penalized very quickly.
Paying for links has always been frowned upon, but on the back of recent Google updates, particularly Google Penguin, it is now a big problem for any site that has carried out this practice.
Links should be natural; paying for them isn’t and Google can tell the difference.
If you have paid for any links in the past, remove or ‘nofollow’ these links as soon as you can. If you are unable to do this, consider disavowing the domain using the Google Disavow Tool, so that Google doesn’t take it into account when reviewing your link profile.
Don’t pay for getting links.
Does a High PageRank Mean High Rank in Search Engines?
No, it doesn’t.
There are thousands of examples out there that show pages with a low PageRank outrank pages with a far higher score.
The truth is PageRank is an out-of-date metric that doesn’t really mean anything anymore.
In its simplest form; PageRank is calculated by the number of links a page is receiving. The value of the page linking to you is also taken into consideration.
It can be a small indicator that you are on the right track, but beyond that, you should mainly ignore it.
PageRank is no longer updated, so new sites won’t even be given a PageRank. This is an antiquated metric that is only valuable as a guide for older sites.
I Need As Many Links As Possible
Following quickly on the heels of PageRank, if it were simply about how many links you could build, it would be open season. It’s all about quality, not quantity.
It’s about where your links come from, the value of the site they come from, the nature of your links – are they natural?
Based on the link building section of this guide, do you have the link balance right? Are you over-optimizing towards a certain term? Are you building your brand with these links?
It is better to spend quality time gaining a quality link than creating a ton of bad and irrelevant links.
Having millions of links doesn’t guarantee you great rankings; quality links are much more likely to.
Do I need to Optimize Meta Keyword Tag?
Don’t waste your time. Google doesn’t read this tag anymore and doesn’t pay any attention to it.
In fact, having meta keyword tags could be detrimental, as the only thing they do is give your competitors an idea of the keywords you’re trying to rank for.
Remove all waste in your coding and let Google get to the good stuff quickly.
I Need A Keyword Density of Around 2% to 3%
Change this to ‘Have I written for my audience?’ and you will be on the right track.
Keyword density used to be all the rage, but times have changed. It shouldn’t be about how many times you can include a key term in your content.
Write for your audience.
If you are naturally writing about a certain subject, product, or service, your targeted terms will naturally be included (which will add this important relevance to your page).
A great rule of thumb we always try to abide by is:
‘If you were to hand a stranger your content, could they pick which terms you were working with?’
If the answer is yes, you are over-optimizing. These terms are standing out when instead your content should be natural.
Google AdWords Influences Organic Rankings
This is a conspiracy theory that continues to linger. Regardless of what you have read or what your friend ‘in the know’ has said; there is no connection at all between AdWords and organic listings.
One does not have any influence over the other.
You can have the most amazingly run AdWords account, but it will have no knock-on effect on your organic rankings.
You can have the most perfectly optimized SEO campaign and have top rankings across the board, but this won’t improve your AdWords account in any shape or form.
It is as simple as that.
‘Nofollow’ Links Are Totally Useless
Nofollow links are links that contain the rel=”nofollow” attribution within the link’s coding.
Basically, this command informs search engines not to pass any link strength to the linked-to page.
As a result, it is often believed that gaining such links is a waste of time.
This train of thought couldn’t be more wrong.
Having a percentage of ‘nofollow’ links helps to highlight that you have a natural and healthy link profile. If none of your links were ‘nofollow’, how unnatural would that look?
In addition, it isn’t just the ‘link juice’ value that makes a link valuable; the link could be delivering strong, relevant referral traffic too, and the nofollow attribute doesn’t affect that.
I Should Try and Rank For Misspellings
Once upon a time, this used to be all the rage, trying to capture all the traffic created by people who misspelt a key term or even a company name. Sites even used to have completely separate but near-identical pages for the misspelt keyword variations.
This is a very poor practice in modern SEO that will do you more harm than good.
In order to rank for a misspelling, the belief was that you needed to have optimized a page for that version. Do you really want to have a misspelling on your site just to capture this small percentage? No: it looks unprofessional.
Algorithms have also become a lot smarter and will be pointing out these mistakes to the searcher and giving them the correct alternative, so don’t worry.
SEO Isn’t About Usability
There are two ways of looking at this.
If you aren’t taking usability into account, regardless of whether you believe it to be an SEO factor or not, you are going to lose custom.
In addition, if you don’t believe that Google is clever enough to take usability into account, you are going to lose valuable ranking space.
Whichever way you look at it, usability is hugely important.
Remember, Google wants you to create a site that is for the visitors, not the search engines. If you don’t do that, Google won’t be paying much attention to you either.
If users click on your site from the SERPs and can’t use your site or find what they’re looking for, they’re likely to bounce right back to the search engines. This in itself is a negative signal to Google that your site doesn’t deliver value.
Focus on the user and make it easy for them to find what they’re looking for.
Can an SEO Agency Guarantee Me First-Place Rankings?
Put simply, no they can’t. No one can.
Keep well away from anyone who says they can.
Google is a third-party site and only it knows completely how the algorithm works.
There are no partners and no preferred agencies that can gain better rankings as a result.
Backstreet agencies may well be able to get you top of the rankings very quickly through spammy tactics, but soon enough you will drop like a stone with a penalty that will make it very hard for your site ever to rank well again.
Don’t risk it.
SEO is a long-term project; there are no real shortcuts and it needs to be done properly.
Summary
According to a lot bloggers, SEO has been dead for a very long time. The truth is it isn’t and never will be. SEO as we knew it back in 2002 is different from what people were doing in 2009. SEO today is again very different than in 2009.
No matter what tactics and algorithms come and go, what signals become redundant, and what ground-breaking new elements become big-game players, sites will always need strong search engine exposure to maximize their success.
That will never change and without strong, relevant information and content, search engines won’t be able to truly marry up whatever external factors are adding strength to your site.
SEO may change, but it will never die.
Having read this post you should now have a strong and well-planned SEO strategy that is sustainable in the long run.


